- Rendering is actually 3 components:
- Light and shadow: How it shows the form of an object
- Material rendering: Showing how the object reflects light.
- Texture rendering: The small forms and contour on an object.
Light and shadow
- This is the fundamental, you need light and shadow to show the form of an object. This is often taught as the usual sphere you see in tutorials.
Material Rendering
- This usually refers to the glossiness and specularity of the object.
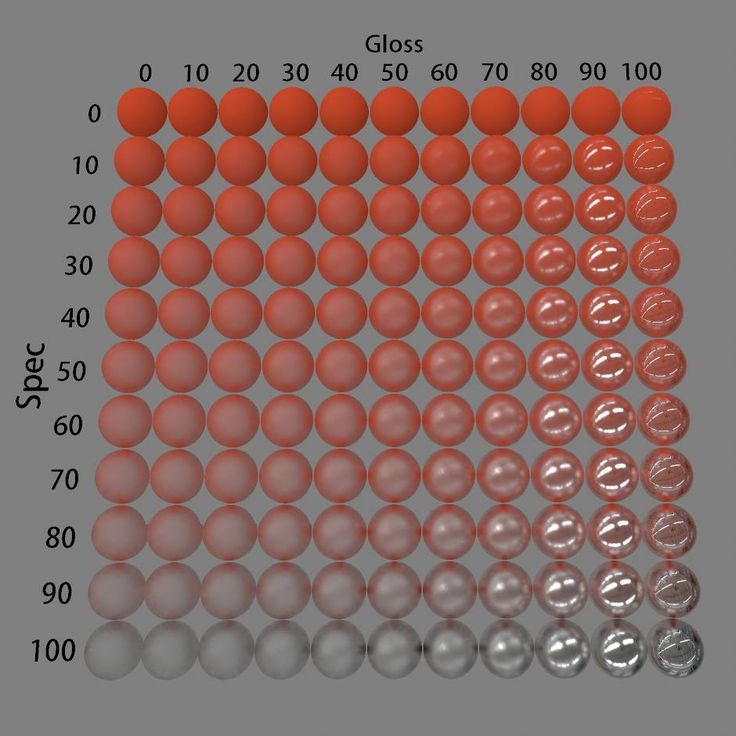
- All materials fall into specific Specularity and Glossiness. (+ transparency)
- Glossiness = smoothness of an object
- A glossy object will have sharp, clean highlights. (ie: it's a smooth object, just like a criminal.)
- A non-glossy object will have blunter highlights. (ie: it's a rough object.)
- Specularity = How well light is reflected off an object
- A specular object will reflect light very well
- A non-specular object will not reflect light very well. (light is absorbed instead of entering out eyes)
- Example: A bumpy metal sphere can reflect light well, but it won't be clear, so it has high specularity but low glossiness.
- Example: A cue ball can doesn't reflect , and it will be clear
Texture Rendering
- Surprisingly, texture is different from material rendering.
- You've probably noticed that freshly chopped wood is very not rough, but.... often wood that is treated is very smooth! (Sanded wood)
- So texture is a separate thing.
- Anyway, texture is basically micro-forms.
Putting it all together
- see this video at this point in time: https://youtu.be/XaVybuZsZs4?si=SpT26QxWw6IjVmt6&t=1067
- Often, you will be layering material and texture rendering over each other over and over again, and that is okay.
- Basically, start from the bottom layer, material render it, add form, material render it, add texture again.
- Also blessed video thank you for not using special brushes. Just hard round one, no gimmicks.
- Also it's single layer.
